Unit 3 Sections 9 and 11
Vocab
- Algorithms: Process or set of rules to followed through code
- condition: is a boolean expression when an expression outputs either true or false
- boolean values: are another type of data in programming languages. can only hold true or false
- Selection: process used in algorithms where a conditional if statement leads to one of two outcomes
- Iteration: process that allows certain things to happen until a condition is satisfied
- Binary Search: search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
- Bits: most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications
- byte: a group of binary digits or bits (usually eight) operated on as a unit
- hexadecimal: relating to or using a system of numerical notation that has 16 rather than 10 as its base.
temp = int(input("Select a temperature from 0 to 99 degrees F"))
if (temp >= 90):
print("It's too hot outside!")
else:
if (temp >= 65):
print("Sure I will play outside!")
else:
print("It is too cold outside!")
temp = int(input("Select a temperature from 0 to 99 degrees F"))
if (temp >= 90):
print("It's too hot outside!")
if (temp >= 65):
print("Sure I will play outside!")
if (temp < 65):
print("It is too cold outside!")
- Conditionals vs. Booleans
- condition is a boolean expression when an expression outputs either true or false
- boolean values are another type of data in programming languages. can only hold true or false
IsHoliday = False
IsWeekday = True
if IsHoliday:
driveWork = True
else:
if IsWeekday:
driveWork = True
else:
driveWork = False
print(driveWork)
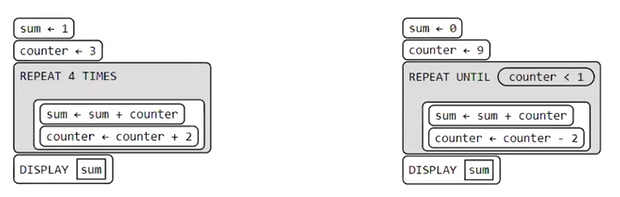
sum = 1
counter = 3
loop = 0
while (loop < 4):
sum = sum + counter
counter = counter + 2
loop = loop + 1
else:
print(sum)
sum = 0
counter = 9
while (counter >= 1):
sum = sum + counter
counter = counter - 2
print(sum)
- Selection
- process used in algorithms where a conditional if statement leads to one of two outcomes
- Iteration
- process that allows certain things to happen until a condition is satisfied
- Algorithm to Start (Determining Whether a Number is Even or Odd)
- Binary Search
- search algorithm that finds the position of a target value within a sorted array.
- Binary search compares the target value to the middle element of the array.
- An algorithm for iterating to find a value inside a data set
- starts in the middle of a data set of numbers and eliminates half the data. This process repeats until the desired value is found or until all elements have been eliminated.
- In order to use binary search effectively and properly, data must be stored in order
- COLLEGE BOARD INDEX STARTS AT 1 NOT 0
def BinarySearch(array, x, low, high):
# Repeat until the pointers low and high meet each other
while low <= high:
mid = low + (high - low)//2 # find the middle (taking the higest index number plus the lowest and divided by two)
if array[mid] == x: # if desired number is the middle is found return desired number (middle number)
return mid
elif array[mid] < x:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
array = [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
x = 4
result = BinarySearch(array, x, 0, len(array)-1)
if result != -1:
print("Element is present at index " + str(result))
else:
print("Not found")
- Binary Search with Iteration
- Compare x with the middle element.
- If x matches with the middle element, we return the mid index.
- Else if x is greater than the mid element, then x can only lie in the right (greater) half sub-array after the mid element. Then we apply the algorithm again for the right half.
- Else if x is smaller, the target x must lie in the left (lower) half. So we apply the algorithm for the left half.
def binary_search(arr, x):
low = 0
high = len(arr)-1
mid = 0
if low<=high:
mid = (low + high) // 2 #integer part
if x == arr[mid]:
return mid
elif x < arr[mid]:
high = mid - 1
return high
else:
low = mid + 1
return low
else:
return -1
arr = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]
x = 11
result = binary_search(arr, x)
if result != -1:
print("Found at position : ",str(result))
else:
print("Not in the array!")
- FlowChart for Situation
- You're playing a short game using a random number generator from 1 to 20
- On each turn, a player will generate 3 random numbers
- They get to keep the highest number that they generate as their score
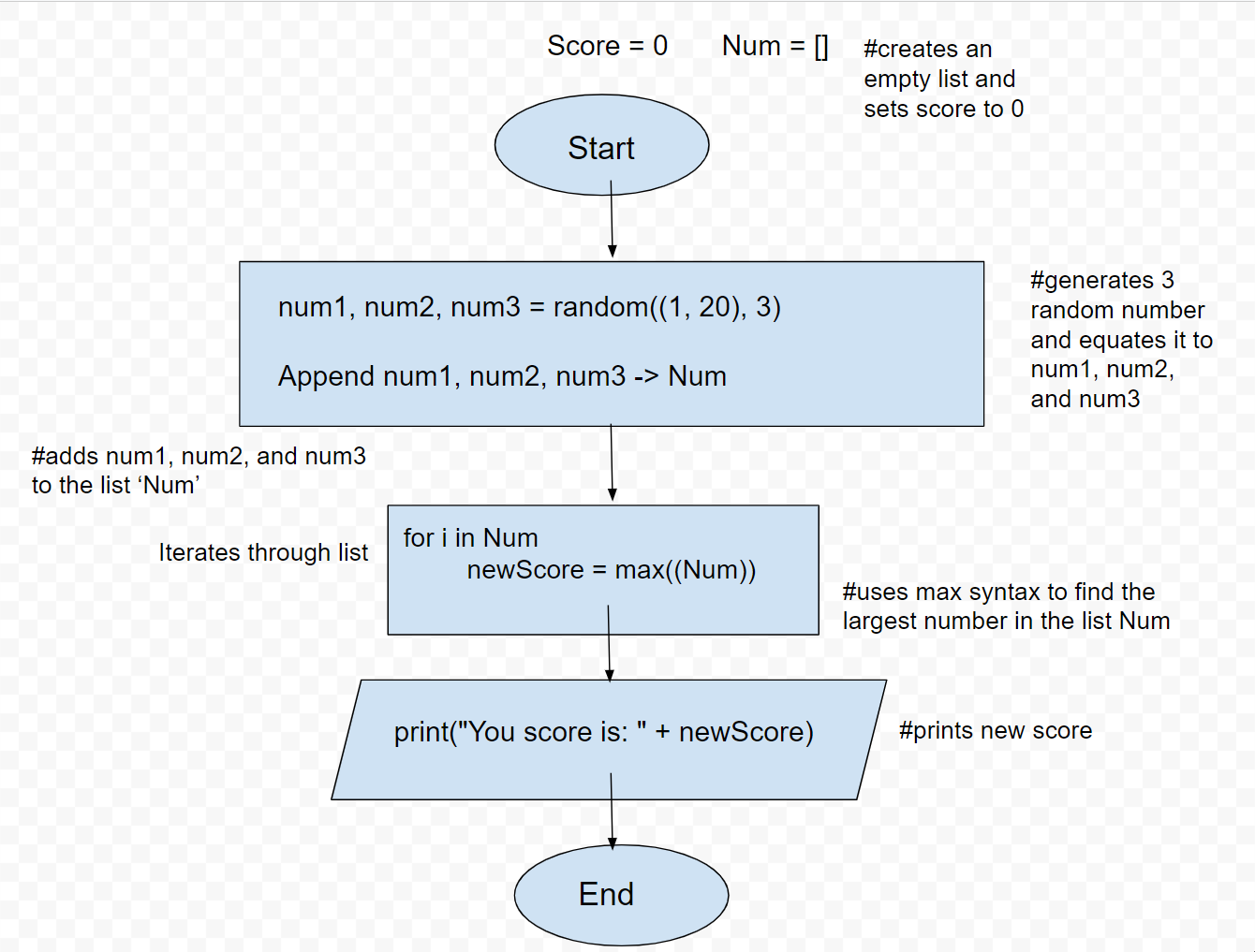
import random
Num = []
Score = 0
num1, num2, num3 = random.sample(range(1, 20), 3) #generates a random number and equates it to num1, num2, and num3
Num.extend([str(num1), str(num2), str(num3)]) #adds num1, num2, and num3 to the list ‘Num’
for i in Num: #iterates through each number in the list Num
newScore = (max(map(int, Num))) #map makes the list a list of integers. uses max syntax to find the largest number in the list Num.
print("You rolled the numbers " + str(Num) + ". Your score is: " + str(newScore)) ##prints new score